Fiscal Policy plays a central role in how governments manage the economy, influence growth, and respond to financial challenges. It refers to the use of government spending, taxation, and borrowing decisions to guide economic activity in a country.
In simple terms, Fiscal Policy is about how much the government spends, how much it collects in taxes, and how it balances the two to achieve economic goals. When applied carefully, it can stabilize the economy, support jobs, and promote long-term development.
What Is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal Policy is a government’s strategy for managing public finances to influence economic conditions. It is set and implemented by national authorities, usually through annual budgets and financial legislation.
By adjusting spending levels and tax rates, governments aim to control inflation, reduce unemployment, and encourage sustainable economic growth. These decisions directly affect households, businesses, and financial markets.
Key Objectives of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal Policy exists to support broader economic and social goals. Governments design fiscal measures to address both short-term economic issues and long-term development needs.
Common objectives include:
- Promoting economic growth and stability
- Reducing unemployment and poverty
- Controlling inflation
- Redistributing income more fairly
- Financing public goods such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure
Each objective reflects the government’s priorities and the economic conditions at a given time.
Types of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal Policy can take different forms depending on whether the government wants to stimulate or slow down the economy. These approaches are usually applied in response to economic cycles.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Expansionary Fiscal Policy is used when the economy is weak or slowing down. The government increases spending, reduces taxes, or does both to encourage demand.
This approach puts more money into the economy, helping businesses grow and supporting job creation. It is commonly used during recessions or periods of high unemployment.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Contractionary Fiscal Policy is applied when the economy is growing too fast, and inflation becomes a concern. The government reduces spending, increases taxes, or combines both measures.
The goal is to slow down excessive demand and prevent prices from rising too quickly. This approach helps maintain long-term economic stability.
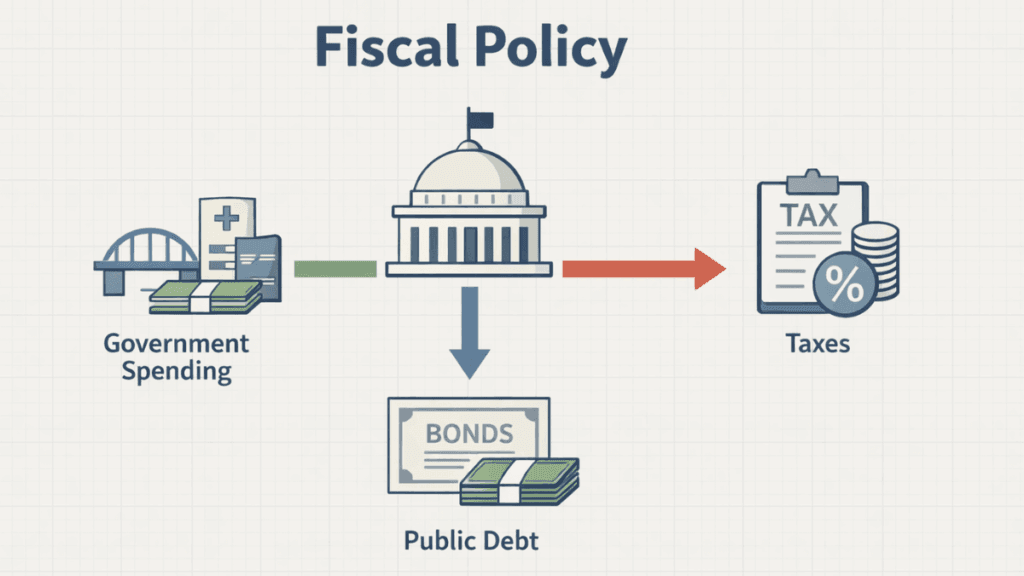
Tools Used in Fiscal Policy
Governments rely on specific tools to implement Fiscal Policy effectively. These tools directly affect how money flows through the economy.
Government Spending
Government spending includes money spent on infrastructure, public services, social programs, and wages. Increased spending can boost economic activity, while reduced spending can help control budget deficits.
Decisions on spending priorities often reflect political choices as well as economic needs.
Taxation
Taxes are a major source of government revenue and a powerful fiscal tool. By adjusting tax rates, governments can influence consumer spending, business investment, and income distribution.
Lower taxes tend to encourage spending and investment, while higher taxes can help cool down an overheated economy.
Public Borrowing
When spending exceeds tax revenue, governments borrow money by issuing bonds or taking loans. Borrowing allows governments to fund large projects or respond to emergencies without raising taxes immediately.
However, excessive borrowing can increase public debt and create long-term financial risks if not managed responsibly.
Fiscal Policy vs Monetary Policy
Fiscal Policy is often discussed alongside monetary policy, but the two are not the same. Each plays a distinct role in economic management.
The government controls Fiscal Policy and focuses on spending and taxation. The central bank manages monetary policy and controls interest rates and money supply.
While they operate separately, both policies work best when they are coordinated. Together, they help maintain economic balance and financial stability.
Automatic Stabilizers in Fiscal Policy
Automatic stabilizers are built-in features of Fiscal Policy that respond to economic changes without new government action. They help smooth out economic fluctuations naturally.
Examples include progressive tax systems and unemployment benefits. During economic downturns, tax payments fall and social spending rises, supporting household incomes and demand.
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Economic Growth
Fiscal Policy plays a vital role in shaping long-term economic growth. Strategic public investment can improve productivity and living standards.
Spending on infrastructure, education, and healthcare strengthens the foundation of the economy. Well-designed tax systems can also encourage entrepreneurship and innovation.
Fiscal Policy and Inflation Control
Fiscal Policy influences inflation by affecting overall demand in the economy. Excessive government spending can increase demand beyond supply, pushing prices higher.
On the other hand, reducing spending or increasing taxes can help slow inflation. Effective fiscal management ensures price stability while supporting growth.
Fiscal Deficits and Budget Surpluses
A fiscal deficit occurs when government spending exceeds revenue. This is common during economic downturns or periods of heavy public investment.
A budget surplus happens when revenue exceeds spending. Surpluses can be used to reduce debt or save for future economic challenges.
Both deficits and surpluses can be appropriate depending on economic conditions and policy goals.
Public Debt and Fiscal Sustainability
Public debt is the accumulation of past fiscal deficits. While borrowing can support growth, long-term sustainability is essential.
Fiscal sustainability means the government can meet its current and future obligations without causing economic instability. Responsible budgeting and transparent financial management are key to maintaining trust and stability.
Fiscal Policy in Developing Economies
In developing economies, Fiscal Policy is often used to address structural challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and inadequate infrastructure. Government spending plays a crucial role in building essential services.
However, limited tax bases and high debt levels can constrain fiscal options. Careful planning and efficient use of resources are especially important in these contexts.
Political and Social Influences on Fiscal Policy
Fiscal Policy decisions are not purely economic. They are shaped by political priorities, public opinion, and social needs.
Election cycles, social pressures, and ideological beliefs can influence how governments design budgets and allocate resources. This makes transparency and accountability essential for effective fiscal governance.
Challenges and Limitations of Fiscal Policy
While powerful, Fiscal Policy has limitations that must be recognized. Poorly designed policies can lead to inefficiencies and long-term problems.
Common challenges include:
- Delays in policy implementation
- Rising public debt
- Political constraints
- Inefficient allocation of resources
Understanding these limits helps policymakers design more effective and balanced fiscal strategies.
Why Fiscal Policy Matters to Everyday Life
Fiscal Policy affects daily life more than many people realize. It influences job opportunities, prices, public services, and overall economic security.
From roads and schools to taxes and social programs, fiscal decisions shape the quality of life in a country. Understanding Fiscal Policy helps citizens make informed decisions and engage meaningfully in economic discussions.
Conclusion
Fiscal Policy is a cornerstone of modern economic management. Through careful control of spending, taxation, and borrowing, governments can guide economies toward stability and growth.
When used responsibly, Fiscal Policy supports development, protects vulnerable groups, and strengthens public trust. A clear understanding of its role helps individuals, businesses, and policymakers navigate economic challenges with greater confidence.