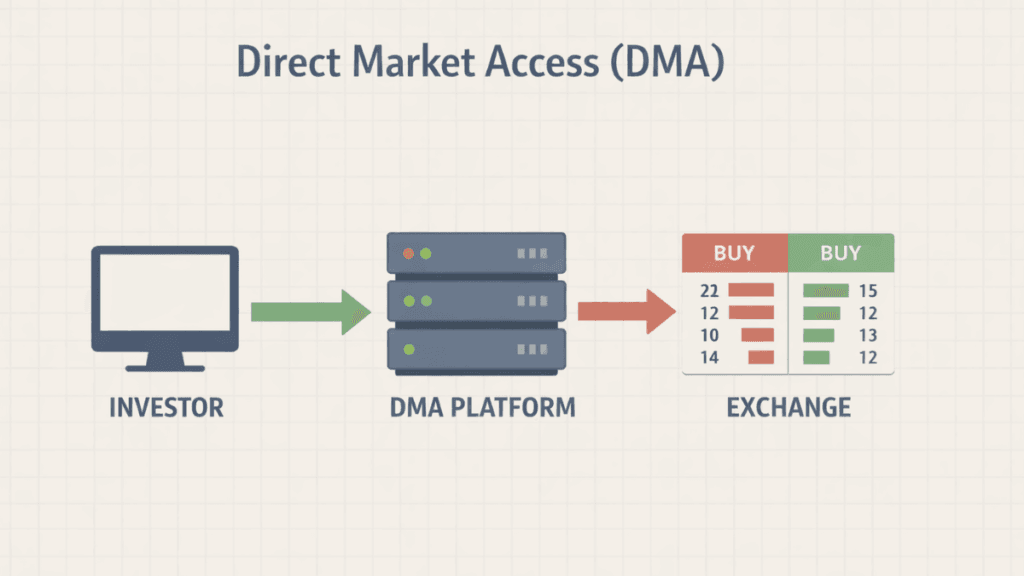
Direct Market Access (DMA) is a trading setup that allows investors to place orders directly into a financial market’s order book without a broker manually intervening. In the first interaction with a DMA platform, traders experience faster execution, greater transparency, and more control over how their trades reach the market, which is why professional and institutional participants widely use Direct Market Access.
Unlike traditional brokerage models, DMA connects traders straight to exchanges or liquidity venues through advanced trading infrastructure. This direct connection changes how orders are executed, priced, and monitored, making it an important concept in modern financial markets.
What Is Direct Market Access?
Direct Market Access refers to a trading arrangement where an investor sends buy or sell orders directly to an exchange or electronic trading venue. The broker still provides the technology and regulatory oversight, but does not decide how or when the trade is placed.
This structure removes the broker’s dealing desk from the execution process. As a result, the trader has full visibility of market depth and can interact directly with available liquidity.
How Direct Market Access Works
Direct Market Access operates through specialized trading platforms that connect users to exchanges in real time. These platforms are typically provided by brokerage firms but are designed for speed, precision, and control.
When a trader submits an order using DMA, the order goes straight to the exchange’s order book. The broker’s role is limited to risk checks, margin monitoring, and regulatory compliance rather than execution decisions.
DMA vs Traditional Brokerage Trading
The difference between DMA and traditional trading lies mainly in control and execution. Traditional brokers may internalize orders or route them through their own systems, while DMA provides a direct path to the market.
With DMA, traders see the same prices and order book data as other market participants. In contrast, traditional trading often involves quoted prices that may include broker markups or delays.
Key Features of Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access platforms are built for precision and transparency. They offer tools that allow traders to interact with markets in a highly granular way.
Common DMA features include:
- Full visibility of the order book and market depth
- Ability to choose order types, timing, and price levels
- Ultra-low latency execution through direct exchange connections
These features are especially valuable for strategies that depend on speed and exact pricing.
Who Uses Direct Market Access?
Direct Market Access is most commonly used by institutional investors and professional traders. These participants typically trade large volumes and require advanced execution capabilities.
Hedge funds, asset managers, proprietary trading firms, and some experienced retail traders rely on DMA to implement complex strategies. Beginners usually start with standard brokerage accounts before moving to DMA as their knowledge grows.
Markets That Support Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access is available across many major financial markets. Each market uses DMA slightly differently, but the core principle remains the same.
DMA is commonly used in:
- Equity markets such as stocks and exchange-traded funds
- Futures and derivatives markets
- Foreign exchange (FX) through electronic communication networks
- Some cryptocurrency exchanges with professional-grade access
Availability depends on local regulations and the broker’s infrastructure.
Benefits of Direct Market Access
One of the main advantages of Direct Market Access is execution speed. Orders reach the market with minimal delay, which can reduce slippage and improve pricing.
DMA also increases transparency by showing real-time market depth. Traders can see where liquidity is concentrated and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risks and Limitations of Direct Market Access
While DMA offers many benefits, it also introduces additional responsibility. Traders must understand how markets function, as poor order placement can lead to unexpected losses.
Another limitation is cost. DMA accounts often require higher minimum balances, platform fees, or commission structures that are not suitable for casual traders.
Regulatory Oversight and Compliance
Direct Market Access is closely regulated in most financial jurisdictions. Regulators require brokers to implement strict risk controls even though traders place orders directly.
These controls include pre-trade risk checks, position limits, and automated monitoring. The goal is to prevent market abuse, excessive risk-taking, and system-wide disruptions.
Technology Behind Direct Market Access
DMA relies on advanced trading infrastructure designed for speed and reliability. This technology includes high-performance servers, low-latency network connections, and sophisticated order management systems.
Many professional traders colocate their servers near exchange data centers to reduce execution delays. While retail users do not need this level of setup, the same technology principles support their DMA platforms.
Costs Associated With Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access pricing is usually more transparent than traditional brokerage models. Instead of wider spreads, traders often pay explicit commissions.
Costs may include exchange fees, platform fees, and data subscription charges. Understanding these costs is essential before choosing a DMA provider.
Direct Market Access in Algorithmic Trading
DMA plays a central role in algorithmic and quantitative trading. Automated strategies rely on direct execution to function correctly and consistently.
Because DMA provides precise control over order placement, algorithms can respond to market conditions in milliseconds. This level of access is critical for high-frequency and statistical trading strategies.
Is Direct Market Access Suitable for Beginners?
Direct Market Access is not typically recommended for complete beginners. The learning curve is steeper, and mistakes can be costly without broker intervention.
However, motivated learners who invest time in understanding market structure may eventually benefit from DMA. Many traders transition to DMA after gaining experience with standard trading platforms.
Choosing a Direct Market Access Broker
Selecting the right DMA broker requires careful evaluation. The quality of execution, platform stability, and regulatory standing all matter.
A reliable DMA broker should offer transparent pricing, strong risk controls, and access to reputable exchanges. Educational resources and customer support are also important, especially for newer users.
Real-World Example of Direct Market Access
Consider an institutional trader buying shares of a large company. Using DMA, the trader can place limit orders at specific price levels directly into the exchange’s order book.
This approach allows the trader to minimize market impact and control execution timing. Without DMA, the same order might be executed at less favorable prices through a broker’s internal system.
The Future of Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access continues to evolve as markets become more electronic and interconnected. Advances in technology are making DMA faster, more accessible, and more efficient.
As transparency and competition increase, DMA is likely to remain a cornerstone of professional trading. Its emphasis on control and direct participation aligns closely with the direction of modern financial markets.
Final Thoughts on Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access represents a powerful way to interact with financial markets. By removing unnecessary intermediaries, it offers speed, transparency, and precision for those who know how to use it.
For traders willing to learn and manage the added responsibility, DMA can be a valuable tool. Understanding its mechanics, risks, and costs is the key to using Direct Market Access effectively and responsibly.